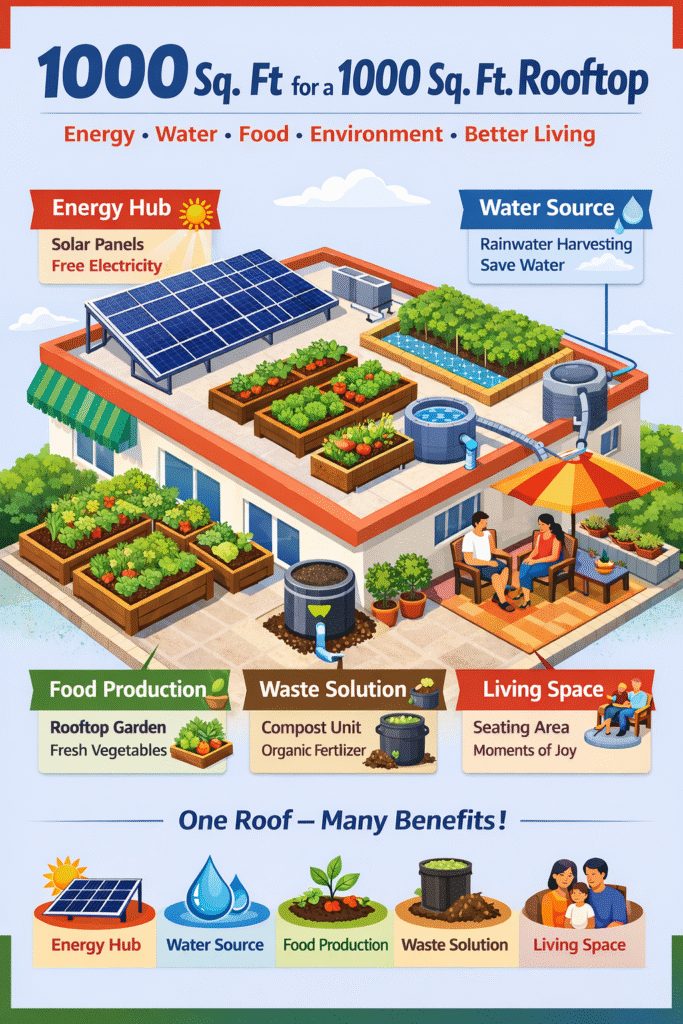
🏡Best Combination of Roof (एक आदर्श मॉडल)
एक ही छत पर ऊर्जा, पानी, भोजन, खाद और आराम – सब कुछ संभव है। भूमिका (Introduction) आज का युग महंगाई, बेरोज़गारी, ऊर्जा संकट और जल संकट का युग है। हर परिवार चाहता है कि उसका खर्च कम हो, आय बढ़े और जीवन स्तर सुधरे। लेकिन ज़्यादातर लोग यह नहीं जानते कि इसका समाधान उनके अपने घर की छत पर मौजूद है। हमारी छत आज भी अधिकतर घरों में खाली पड़ी रहती है—केवल धूप, गर्मी और बारिश सहने के लिए। जबकि यदि उसी छत को स्मार्ट तरीके से उपयोग किया जाए, तो वही छत: यह ब्लॉग आपको एक आदर्श “Best Combination Roof Model” से परिचित कराएगा, जिसे अपनाकर आम नागरिक स्वावलंबी (Self-Reliant) बन सकता है। आदर्श मॉडल क्या है? (What is Best Combination Roof) Best Combination Roof का अर्थ है –👉 एक ही छत पर कई उपयोगों को संतुलित रूप से अपनाना, ताकि: इस मॉडल के 5 मुख्य स्तंभ 1️⃣ Solar Panels – छत से कमाई जाने वाली बिजली Solar क्यों ज़रूरी है? बिजली का बिल हर महीने बढ़ रहा है। ऐसे में सोलर पैनल: आम घर के लिए कितना सोलर? सिस्टम उपयोग 1 kW पंखा, लाइट, टीवी 2 kW फ्रिज, मोटर, वॉशिंग मशीन 3 kW पूरा मध्यम घर आर्थिक लाभ आय कैसे हो सकती है? 👉 Solar = खर्च में कटौती + भविष्य की सुरक्षा 2️⃣ Rain Water Harvesting – छत से पानी का खजाना समस्या आज कई शहरों में: समाधान – Rain Water Harvesting छत पर गिरने वाला बारिश का पानी: के ज़रिए संग्रह किया जा सकता है। कितना पानी मिल सकता है?☔ 1000 Sq Ft Roof से Rainwater Harvesting Calculation 🔢 Step 1: Roof Area को समझें 👉1000 sq ft × 0.0929 = 92.9 sq meter 🌧 Step 2: Average Rainfall मान लें भारत के ज़्यादातर हिस्सों में average rainfall: 👉Rainfall Height = 1 meter 💧 Step 3: पानी की कुल मात्रा (Basic Formula) 📌 Formula: Water Collected (Liters) = Roof Area (sq m) × Rainfall (m) × 1000 Calculation: = 92.9 × 1 × 1000= 92,900 Liters 👉 अगर 100% पानी इकट्ठा किया जाए तो = 92,900 लीटर ⚙️ Step 4: Practical Losses को जोड़ें असल जीवन में: इसलिए हम 80% efficiency मानते हैं। 92,900 × 80% = 74,320 Liters ✅ (One Season / One Year) 👉 1000 Sq Ft Roof से ≈ 70,000 – 75,000 लीटर पानी एक मानसून सीज़न में आसानी से स्टोर किया जा सकता है। 🏠 यह पानी कितने काम आएगा? उपयोग कितने दिन 4 लोगों का घरेलू उपयोग 4–6 महीने Terrace Garden पूरा साल Toilet + Cleaning 6–8 महीने Groundwater Recharge लंबे समय तक 💡 आसान भाषा में समझें 🧠 याद रखने वाला Shortcut Formula हर 100 sq ft छत ≈ 7,000–8,000 लीटर पानी / वर्ष तो: 🌱 निष्कर्ष 👉 1000 sq ft की छत = पानी का छोटा तालाब अगर हर घर यह करे: “जो बारिश आज बह जाती है, वही कल जीवन बचा सकती है।” उपयोग आर्थिक लाभ 3️⃣ Terrace Garden – छत से ताज़ा भोजन और कमाई Terrace Garden क्यों? आज हम जो सब्ज़ियाँ खाते हैं: क्या उगा सकते हैं? खर्च और बचत आय का साधन 👉 Terrace Garden = सेहत + बचत + कमाई 4️⃣ Compost Unit – कचरे से सोना समस्या समाधान – Compost Unit 👉 30–40 दिन में जैविक खाद फायदे आय कैसे? 5️⃣ Sitting Area – छत को जीवन का हिस्सा बनाना सिर्फ आराम नहीं, मानसिक स्वास्थ्य सामाजिक लाभ 🔁 यह मॉडल कैसे एक-दूसरे को सपोर्ट करता है? 👉 पूरा सिस्टम एक चक्र में चलता है 💰 कुल आर्थिक प्रभाव (Annual Impact) स्रोत लाभ बिजली बचत ₹15,000–₹40,000 पानी बचत ₹5,000–₹15,000 सब्ज़ी बचत ₹20,000–₹40,000 अतिरिक्त आय ₹30,000–₹1,00,000 👉 कुल संभावित लाभ: ₹70,000 – ₹2,00,000 / वर्ष 🏠 किन लोगों के लिए सबसे उपयोगी? 🌍 सामाजिक और राष्ट्रीय लाभ निष्कर्ष (Conclusion) छत केवल कंक्रीट नहीं है,👉 वह आपका भविष्य है। अगर हर घर अपनी छत को: बना ले, तो भारत: